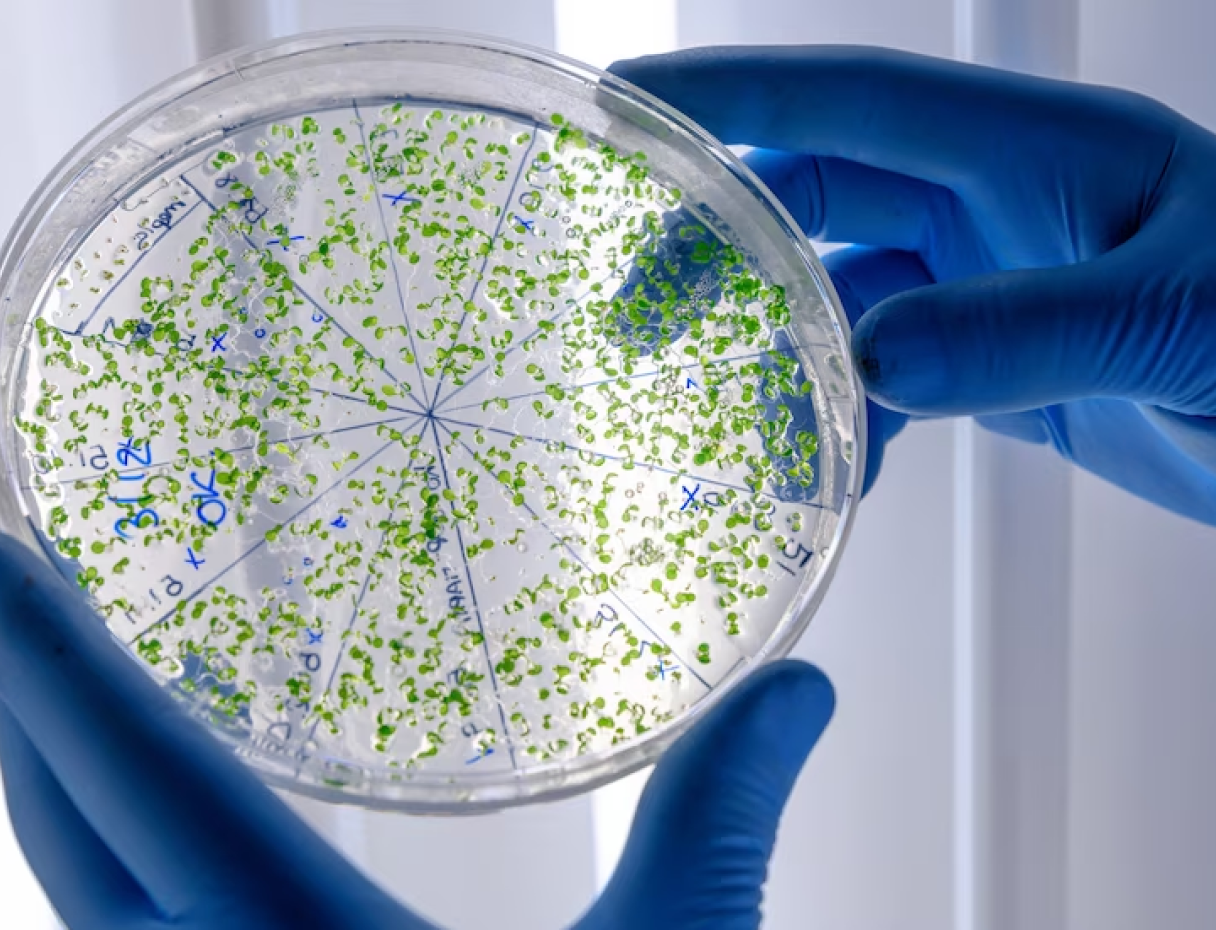
Tissue Culture
Plant tissue culture techniques involve growing plant cells, tissues, or organs in an aseptic environment. This method is used for clonal propagation, where a single plant can be multiplied into many identical copies, ensuring uniformity and preservation of valuable plant traits. Plant tissue culture can be conducted in an organic way by adhering to the principles and practices of organic agriculture. While tissue culture inherently takes place in a controlled laboratory environment, certain aspects can still align with organic values.
Tissue Culture
-
Starting Material:
Choose plant material that comes from organically grown plants. Ensure that the parent plants used for tissue culture have been cultivated using organic practices and haven't been treated with synthetic chemicals. -
Culture Media:
Use organic-certified culture media whenever possible. These media should contain organic ingredients and avoid synthetic chemicals, hormones, and growth regulators that are prohibited in organic agriculture. -
Sterilization:
Practice proper sterilization techniques to prevent contamination. Use organic-approved sterilizing agents or methods to maintain the organic integrity of the process. -
Nutrient Sources:
Use organic sources of nutrients in the culture media. Organic fertilizers, compost extracts, and natural plant-derived substances can be incorporated to provide essential nutrients to the cultured plants. -
Growth Regulators:
Organic plant growth regulators, such as those derived from natural sources or produced through organic methods, should be used to induce growth, differentiation, and organogenesis. -
Pest and Disease Management:
Implement organic pest and disease management strategies within the controlled environment. This could involve the use of beneficial insects, natural predators, or organic-approved microbial products to control any pests or diseases that may arise. -
Transplanting and Acclimatization:
Once tissue-cultured plants are ready for transfer to soil, use organic potting mixes and substrates. Acclimate the plants gradually to natural environmental conditions to ensure their successful transition. -
Documentation and Certification:
Keep thorough records of the organic practices followed during tissue culture. If the end goal is to produce organic plants, the process should be well-documented and adhere to organic regulations to maintain organic certification. -
Research and Experimentation:
Continue to research and explore organic alternatives and methods for tissue culture. Experiment with different organic formulations, nutrients, and growth regulators to optimize results while staying within the bounds of organic practices.
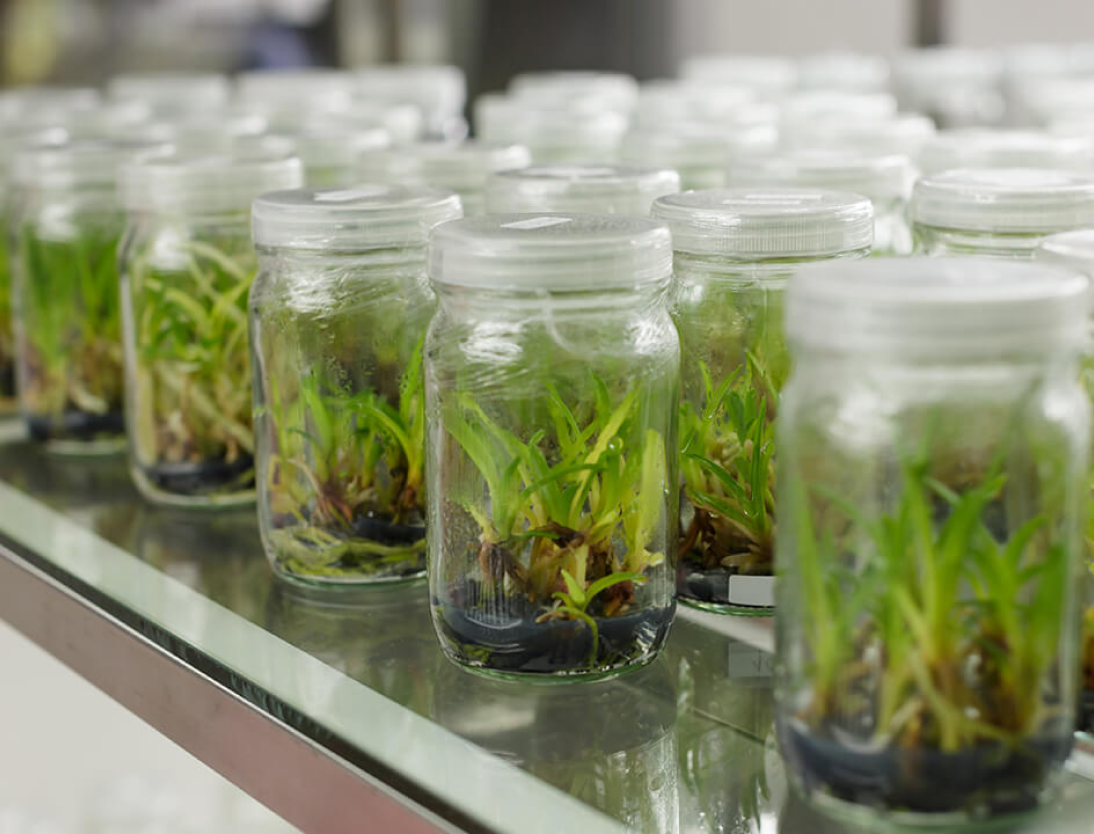

More Benefits
- Tissue culture allows for rapid and efficient clonal propagation of plants. This is particularly valuable for producing large numbers of genetically identical and disease-free plants, ensuring consistency in traits and quality.
- Through tissue culture, plants can be regenerated from disease-free explants, effectively eliminating various diseases and pathogens that may be present in traditional propagation methods.
- Tissue culture enables plant breeders to select and propagate desirable traits, such as disease resistance, improved yield, and unique characteristics, leading to the development of improved plant varieties.
It's important to note that while the principles of organic agriculture can be applied to plant tissue culture, certain challenges may arise. Organic tissue culture may involve more complex nutrient formulations, longer culture times, and potentially higher costs due to the limitations imposed by organic practices. Balancing the requirements of tissue culture with organic principles can be a nuanced process that requires creativity and dedication to both practices.